How should you get the most out of your database cloud migration?
Database migration to the cloud is part of a modern workplace and can provide elasticity and a pay-as-you-go cost model, just like migrating compute resources to the cloud. Yet, it can also improve operational excellence and reliability if you use highly-available cloud-managed database services.
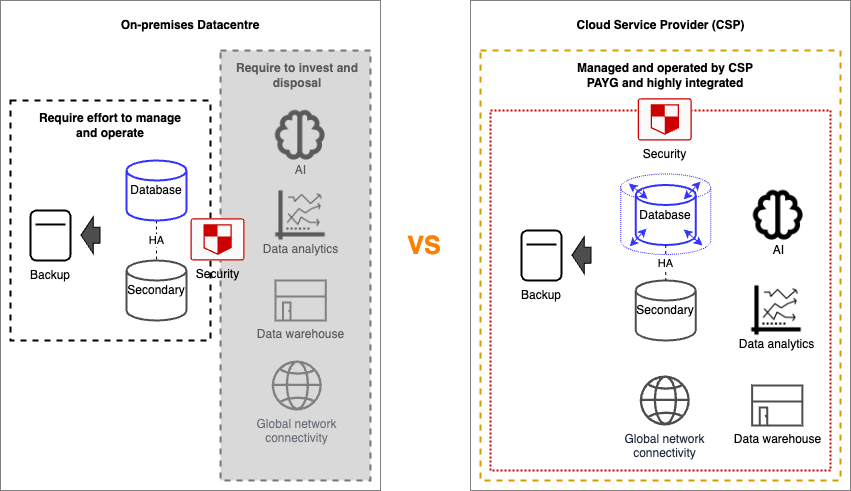
Your database cloud migration can also offer many other benefits like cost savings from licensing, the discovery of business insights via a cloud-native database for data analytics and so on.
However, with different database technologies, migration strategies, methods and tools in existence, it can be challenging to know which combination best suits the needs of your organisation.
Created by experts in cloud transformation, Airwalk Reply, this article explains:
- What database migration to the cloud is
- The benefits of migrating your database to the cloud
- The types of database migration available
- Top tips for migrating your database to the cloud
- Cloud database migration FAQs
1. What is database migration to the cloud?
Database migration is the process of moving your existing database from its traditional setup to a cloud-based environment. It's like giving your database a new home in the cloud, where it can give your organisation all the benefits of cloud computing.
The migration process typically involves planning, analysis, and execution to ensure a smooth transition without data loss or significant disruptions to any application relying on the database. The goal is to take advantage of the benefits offered by cloud computing, such as scalability, flexibility, cost efficiency, and managed services.
During the migration, the database can be moved as-is (lift and shift) or transformed to leverage cloud-native features and services (lift and reshape or even re-architect). Your choice depends on factors within your organisation such as its business needs, current database technology, compatibility with cloud platforms, and specific requirements of your database.
2. What are the benefits of moving to the cloud?
Migrating your databases to the cloud can be a great way to improve agility, scalability, and security across your organisation.In moving your database to the cloud, you can take advantage of the many benefits of cloud computing, like:
- Reduced infrastructure costs: Cloud computing providers offer a pay-as-you-go pricing model, which can help you save money on your database infrastructure costs.
- Improved scalability: Cloud databases are designed to scale vertically (i.e. up or down) or horizontally (out or in) depending on the database technologies as needed, which can help you meet the changing demands of your business.
- Increased data accessibility: Cloud databases are accessible from anywhere with the right level of connectivity established, usually secured and private, which can make it easier for your employees to access the data they need.
- Enhanced security and compliance: Cloud providers offer a variety of security features and services that can help you protect your data.
- Simplified management and maintenance: Cloud providers take care of the day-to-day management and maintenance of your databases, which can free up your IT team to focus on other tasks.
- The ability to leverage cloud-native analytics and AI capabilities: Cloud providers offer a wide range of analytics and AI services that can help you gain insights from your data and make better business decisions.
-
3. Types of database migration
Database migration to the cloud can be categorised into homogeneous and heterogeneous migrations.
Homogeneous database migration
In general, homogeneous migration means migrating a database to the same database technology, for instance, migration from an on-premises PostgreSQL database to a PostgreSQL database hosted by the cloud provider. The target database can be PostgreSQL, deployed on a virtual machine in the cloud (lift and shift, aka rehost) or a cloud-managed database service (lift and reshape, aka re-platform); e.g. Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL, Google Cloud Database PostgreSQL or Azure Database for PostgreSQL.
Advantages
The major advantage of homogeneous migration is the compatibility of the source and target databases. Since the same technology is used after the migration, the chance and extent you need to modify your application for the target database will be much lower compared to using another database technology. The need for acquiring new skills and/or expertise in another technology would be minimal. This can help you reduce the migration effort, i.e. time and cost.
Disadvantages
However, while you may save time and cost using the same database technology via homogeneous migration, you may restrict yourself from the benefits of utilising other technologies which have more to offer. For example, using a cloud-managed open-source database could deliver better long-term cost benefits (as explained further below). Homogenous migration could also restrict any benefit from migrating relational databases to non-relational databases, to align with the nature of your application.
Heterogeneous database migration
Heterogeneous database migration on the contrary is migration from one database technology to another technology; for instance, from Oracle to MySQL (aka re-architect).
Advantages
The advantage of heterogeneous migration is the opposite of the disadvantage of homogeneous migration. You can enjoy the benefits offered by other technologies, for example, if you migrate from a commercial database to an opensource database managed by a Cloud Service Provider (CSP), not only can you enjoy the cost saving from a database license, you can also reduce the operational burden of managing the database and benefit from enterprise-grade support service from the CSP (depending on the level of the support subscription).
You can also take this opportunity to use different database technologies to align with business needs. For instance, if your business focuses on customer experiences and your existing Online Transaction Processing Database (OLTP) makes it harder for you to analyse your data for improvement, you may migrate your database to an Online Analytical Processing Database (OLAP).
There are many cloud-managed database services for OLAP which can help you improve your operational excellence and discover insights from your data; for example Amazon Redshift, GCP BigQuery and Azure Analysis Services. CSPs already have their holistic spectrum of data services or tools that are designed to help you extract valuable insights from your data, such as data exploration and visualisation, ETL, analytics, ML and AI services and tools. This can help you democratise your data in a pay-as-you-go manner without investing a huge amount of money before you start your data journey.
Disadvantages
On the other hand, heterogeneous migration presents contrasting challenges that counter the benefits associated with homogeneous data migration. Since new database technology is used, compatibility between the existing database and the new database will be much lower compared with that of homogeneous migration. This means an update to the application code will likely be required. Depending on the features used, the extent of the update can be very large. The acquisition of skills for the new database technology may also be needed.
Database migration tools
Fortunately, CSPs have many database migration tools to help with heterogeneous database migration and these tools can also be used for homogeneous database migration.
In general, these tools help when assessing the compatibility between the source and target databases with advice for your choice of migration, converting database schema for the target database, e.g. Schema Conversion Tool (SCT) from AWS and Database Schema Conversion Toolkit (DSCT) from Microsoft, and migrating your data to the target database, e.g. Database Migration Service (DMS) of AWS, Azure and GCP.
4. Top Tips for a successful database migration
| know your business needs and objectives |
First of all, you need to know why you need to migrate your database to the cloud and your goals from a business perspective. Is this because you need to migrate your application to the cloud and the database is part of the application? Do you want to take this opportunity to benefit from migrating to another database technology e.g., leveraging data analytics for customer experience and enhancing scalability to improve your service?
It is important to know your goals and what you want to achieve to make the right decisions for the migration. |
| Know your environment and security requirements |
You need to know your environment to decide your migration strategy. For instance, your current database technology, size of your data, network connectivity, maintenance windows, backup and restore, licensing and support. |
| Know your capabilities |
Your team needs the knowledge, expertise, and experience for both the current database and target database technologies so that they can migrate it from the current database to the target database. They need that to utilise and maintain the target database. So, it is important to assess the capabilities of your team. If required, you can skill up your team or extend it by hiring a consultancy service. |
| Know the available database technologies, migration tools and security services |
After knowing what you need and have, it is time to know your choices i.e. the available database technologies and migration tools that can suit your team’s capabilities, environment and business goals. Similarly, you need to get familiar with the security services provided by cloud service providers. |
| Select the right database technology, type of migration, licensing model and contract, and security services |
Often there are multiple database technologies for different types of migration that can suit your needs. They have different strengths and advantages. You need to analyse your business needs, budget, expected return, existing environment, team’s capabilities, technology gap, the available database options and their costs to choose the one that best fits you. If you choose to migrate to the commercial database technology, you will also need to check which licensing models, i.e. bring your own license (BYOL) or pay-as-you-go (PAYG) cloud provider license, benefit you the most. For instance, if you already have a contract with the database vendor that allows BYOL, you may choose BYOL.
Different organisations have different security policies and requirements. You need to ensure the appropriate cloud security services are used to protect your data and comply with your security requirements.
|
| Select the right migration strategy, method and tools |
Different migration strategies, methods and tools are designed for different database technologies, environments and use cases. For instance, if your data size is small, and can be transferred and imported to the cloud database within the maintenance window, big bang migration strategy, and export and import method could be the right choice.
If your maintenance window is very small and your connectivity supports you to replicate your data to the cloud database, zero downtime migration strategy and tool like Database Migration Service (DMS) of cloud service provider e.g. AWS, Azure or GCP may be your choice.
You need to analyse the target database technology, your environment, and your capability to choose the right migration strategy, method, and tools.
|
| Perform Proof of Concept (PoC) |
PoC enables you to verify whether the target database and migration tools can achieve your goals. This is important before you further invest your money and resources for the migration.
You can also discover the challenges and risks via a PoC. This can help you review your choices of database, migration strategy and tools, and have a better plan for the migration.
|
| Strengthen your team and environment to fill the gap if required |
If your team does not have the expertise for target database technology, corresponding tools and cloud services, you will need to upskill it or hire a consultancy service.
Similarly, if your environment cannot support the requirements for the migration strategy, you will need to enhance it e.g. increase the network connection bandwidth for a zero downtime migration strategy.
|
| Perform the migration as planned and post-migration fine-tuning |
Failing to plan is planning to fail. You need to plan for the migration e.g. date and time, availability of the team, risk, backup and fallback. Don’t forget the test plan. A good migration plan can help to guide you through the migration and control risks. However, it is nothing if you do not follow the plan, so it is important to stick with the plan for the migration.
In case, the migration fails, the plan should tell you under what situation and when you should fall back. This helps you reduce the risks and impact of migration failure. Congratulations, if you successfully migrated your database to the cloud as planned. Don’t forget to fine-tune it to ensure its performance and cost are optimised.
|
5. FAQs on database migration
Q What should you look for in a good cloud migration?
Migrating your databases to the cloud can be challenging. Below are some of the biggest hurdles you may face during your database migration.
Choice of database technology
It is vital to choose your database technology correctly and hence the type of database migration for your business needs. Fortunately, there are various database technologies available on the cloud. You need to choose the one that aligns with your goals and needs.
Security
Another big challenge is ensuring that your data is secure. You need to carefully evaluate the security features and services offered by the cloud provider to ensure that your data is protected.
Compatibility
Ensuring that your databases are compatible with the cloud platform is also important. Not all databases are compatible with all cloud platforms. You need to make sure that your databases are compatible with the cloud platform you choose.
Q. How do I move my database to the cloud?
Below are the high-level steps about how to move your database to the cloud.
- Analyse and select the target cloud database technology, migration strategy and security protections based on your business objectives, environment, security requirements, capabilities, available cloud database options, migration tools and cloud security services
- Perform PoC to verify your choice of technology, and discover the challenges and risks. Review your choices of technologies and migration strategy
- Strengthen your team’s capabilities, e.g. upskill and increase bandwidth for network connection
- Analyse the compatibility of your source database and the target database. This can be aided by cloud service provider tools
- Prepare for the migration:
- Getting the cloud database ready e.g. provisioning the database instance, IAM configuration and security protections
- Fixing database and application compatibility issues e.g. schema conversion and application update
- Having an appropriate network connection to the cloud database
- Usually, if your database is used by the application, you will also need to prepare to migrate your application cloud simultaneously
- Plan for the migration, switch over and fallback in case the migration fails
- Testing and validating the migration and fallback in a non-production environment
- Migrate the data to the cloud database and perform a consistency check
- Switch over to the cloud database
- Test and validate the migration. Fallback if required
- Monitor and fine-tune the database
Q. Why migrate a database to the cloud?
- Cost optimisation via pay-as-you-go
- Improve operational excellence by using cloud-managed database service to simplify management and maintenance
- Enhance scalability e.g. scale up/down for RDBMS and scale in/out for NoSQL
- Improve reliability by using HA or replica
- Embrace the database and corresponding technologies based on your business objectives e.g., data analytics and AI, and benefit from the integration with these technologies to leverage the business values from your data
- Better accessibility as cloud service providers can provide database services in various regions and provide connectivity for users and applications from different locations.
Q. What are the three main database migration strategies?
Big Bang – this migration strategy transfers all data in one Big Bang i.e. one operation. The operation and arrangement are simple for this strategy. Required downtime and available maintenance window for migration should be considered.
Trickle – the contrary to Big Bang, this strategy divides the migration into different phases. The source and target databases run and provide service in parallel until all migration phases are complete. This migration strategy requires less downtime however, the operation and organisation for the migration will be more complex.
Zero Downtime – this strategy replicates data to the target database continuously until switched over. The source database provides service until the service is switched over to the target database. Hence, zero or nearly zero downtime will be required. This strategy will require network connectivity with sufficient bandwidth to replicate the data to the target database.
Q. What are the best methods to migrate the database to the cloud environment?
Different database migration methods help you migrate your database to the cloud in scenarios to achieve different objectives for different migration strategies.
One of the common methods is replication-cutover which is often used for the zero downtime migration strategy. Many cloud service providers have tools for this type of migration e.g. Database Migration Service (DMS) of AWS, Azure and GCP. Database vendor tools are also available. Appropriate network connectivity and database compatibility are the key considerations when using this method.
Another common method is export and import. This method is easy and simple for migration to the same database engine and is often used for the big bang migration strategy.
The key consideration is the downtime required to export and import the database. You will normally stop providing service until the cloud database is ready to maintain the consistency of the data.
There are other migration methods suitable for other scenarios. You need to consider different factors, e.g., compatibility, network connectivity, data size and downtime, in order to choose the migration method that best fits your situation.
Conclusion
When migrating your database to the cloud there is no simple equation to tell you how you can get the most out of it.
Should you perform homogeneous database migration to save time and cost during the migration? Or should you perform heterogeneous migration to a cloud-native database to benefit from; data analytics for long-term business planning, new technologies that may better suit your application needs, and cost savings by transitioning licenses to open source?
You need to decide what database technology is the best for your chosen type of database migration. Whether zero-downtime migration strategy is the best for the selected database technology? Is a cloud service provider’s Database Migration Tool the best choice for a zero-downtime migration strategy? What security services should you use to protect your data and comply with your security requirements? These all really depend on your business needs, technology gaps, skills, expertise, requirements, resources, etc.
You should consider the above in conjunction with the cloud database technologies, migration tools and security services available, and that best align with your business goals and requirements. If you still have doubts you should liaise with an appropriate consultant, to ensure that you obtain the maximum benefit from the migration.
Airwalk Reply Cloud Migration Service
Migrate your workloads to the cloud with Airwalk Reply.
We offer a comprehensive cloud migration service that can help you assess your needs, develop a migration plan, and migrate your workloads to the cloud smoothly and securely. Contact us today to learn more.
Additional benefits of using Airwalk Reply's cloud migration service
Expertise - We have a team of experienced cloud migration experts who can help you assess your needs and develop a migration plan that meets your specific requirements. This can help you to ensure things go smoothly, save time and ensure skills/knowledge transfer.
Security - We use the latest security technologies to protect your workloads and data during the migration process and after the migration.
Peace of mind - Our cloud migration service offers expertise, frameworks, and support to help you seamlessly and securely migrate to the cloud. We provide guidance in developing a migration strategy, implementing a practical plan, and delivering the necessary components for cloud success. This ensures your peace of mind throughout the process.
Drop us a message to learn more about our cloud migration service and how we can help you move your workloads to the cloud.
Cloud Migration and Strategy Read more
